Cantargia reports preclinical data highlighting advantages of nadunolimab mechanism of action
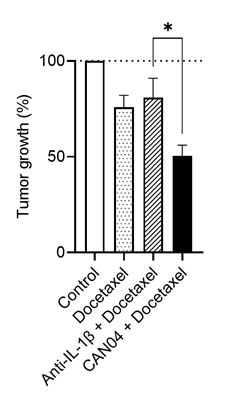
Cantargia AB today report new preclinical data on the antibody nadunolimab (CAN04) in combination with the chemotherapy docetaxel. CAN04 increased the anti-tumor effect of docetaxel, but notably, this was not achieved by blocking only one of the pathways targeted by CAN04, using an antibody against IL-1β signaling. Additionally, docetaxel and other chemotherapies induce the release of the other form of IL-1, IL-1α, by tumor cells. These data highlight the potential of CAN04, which blocks both IL-1α and IL-1β, to increase chemotherapy efficacy. CAN04 is entering clinical development in combination with docetaxel for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Cantargia develops antibody-based pharmaceuticals against interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP). The IL1RAP-binding antibody CAN04 is Cantargia’s most advanced program and is currently investigated in multiple clinical trials in combination with chemotherapy for treatment of cancer. CAN04 is unique compared to other IL-1-targeting concepts as it has a broader mechanism of action. CAN04 mediates killing of IL1RAP-expressing tumor cells via Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) and blocks tumor-promoting signals from both IL-1α and IL-1β. While IL-1β is known to be capable of stimulating tumor growth by various mechanisms, studies have indicated that IL-1α is essential for maintaining a tumor-promoting inflammatory state and may induce resistance to chemotherapy1,2.
Several approaches to block the activity of the individual components of the IL-1 system are assessed clinically. Clinical studies investigating treatment of cancer combining such agents with various chemotherapies are ongoing. A standard therapy for cancer treatment, including late-stage NSCLC, is the chemotherapy docetaxel. The new preclinical data show that CAN04 potentiates the efficacy of docetaxel in mice with established subcutaneous MC38 tumors. The potentiating effect was also compared to antibody blockade of only IL-1β, which in this model did not add any benefit to docetaxel.
Furthermore, in vitro data also demonstrate that addition of chemotherapy to tumor cells increases both the gene expression as well as the release of IL-1α by these cells. Turning to previous observations on the role of IL-1α in mediating resistance to chemotherapy2, these data could indicate that blocking signals from both forms of IL-1 by CAN04 is a key feature of its mode of action for improving chemotherapeutic sensitivity of tumors.
Cantargia intends to present these data at a future scientific conference.
“This new data set is very intriguing and strongly supports the strategy to combine CAN04 with docetaxel for treatment of lung cancer in the upcoming CESTAFOUR clinical trial”, said Göran Forsberg, CEO of Cantargia.
References:
1Tjomsland et al, Neoplasia 2011, 13:664-675
2Liu et al, Cancer Res 2018, 78(8):2040-2051
For further information, please contact
Göran Forsberg, CEO
Telephone: +46 (0)46-275 62 60
E-mail: goran.forsberg@cantargia.com
This is information that Cantargia AB is obliged to make public pursuant to the EU Market Abuse Regulation. The information was submitted for publication, through the agency of the contact person set out above, at 14.30 CET on 30 August 2021.
About Cantargia
Cantargia AB (publ), reg. no. 556791-6019, is a biotechnology company that develops antibody-based treatments for life-threatening diseases. The basis for this is the protein IL1RAP that is involved in a number of diseases and where Cantargia has established a platform. The main project, the antibody CAN04, is being studied clinically as combination therapy with chemotherapy or immune therapy with a primary focus on non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer. Positive interim data from the combination with chemotherapy indicate stronger efficacy than would be expected from chemotherapy alone. Cantargia’s second project, the antibody CAN10, addresses treatment of serious autoimmune/inflammatory diseases, with initial focus on systemic sclerosis and myocarditis.
Cantargia is listed on Nasdaq Stockholm (ticker: CANTA). More information about Cantargia is available at www.cantargia.com.
About nadunolimab (CAN04)
The antibody CAN04 binds strongly to the target IL1RAP and functions both through ADCC as well as blocking IL-1α and IL-1β signaling. Thereby, CAN04 can counteract the contribution of the IL-1 system to the immune suppressive tumor microenvironment and development of resistance to chemotherapy. CAN04 is investigated in three ongoing clinical trials. In the first phase I/IIa-study, CANFOUR, first line combination therapy is investigated using two different standard chemotherapies in patients with NSCLC (gemcitabine/cisplatin) and patients with PDAC (gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel), as well as monotherapy in late stage patients (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03267316). Phase I monotherapy data from 22 patients were presented at ASCO 2019 and showed good safety with infusion-related reaction being the most common side effect. In addition, the biomarkers IL-6 and CRP decreased during treatment. Positive interim data from the combination therapies show durable responses or pseudoprogression in patients with PDAC, resulting in iPFS of 7.8 months, and also a higher response rate of patients with NSCLC, compared to chemotherapy alone. A phase I study, CAPAFOUR, was initiated in H1 2021 and will investigate CAN04 in combination with the chemotherapy regimen FOLFIRINOX for first line treatment of metastatic PDAC (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04990037). A phase I study, CIRIFOUR, is also currently investigating CAN04 in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor and was started H2 2020 (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04452214). Additional clinical combination studies are planned to start during 2021.


